Diabetes, often referred to by doctors as diabetes mellitus, describes a group of metabolic diseases in which the person has high blood glucose (blood sugar), either because insulin production is inadequate, or because the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin, or both. Patients with high blood sugar will typically experience polyuria (frequent urination), they will become increasingly thirsty (polydipsia) and hungry (polyphagia).
Fast facts on diabetes
Here are some key points about diabetes. More detail and supporting information is in the main article.
- Diabetes is a long-term condition that causes high blood sugar levels.
- In 2013 it was estimated that over 382 million people throughout the world had diabetes (Williams textbook of endocrinology).
- Type 1 Diabetes – the body does not produce insulin. Approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1.
- Type 2 Diabetes – the body does not produce enough insulin for proper function. Approximately 90% of all cases of diabetes worldwide are of this type.
- Gestational Diabetes – this type affects females during pregnancy.
- The most common diabetes symptoms include frequent urination, intense thirst and hunger, weight gain, unusual weight loss, fatigue, cuts and bruises that do not heal, male sexual dysfunction, numbness and tingling in hands and feet.
- If you have Type 1 and follow a healthy eating plan, do adequate exercise, and take insulin, you can lead a normal life.
- Type 2 patients need to eat healthily, be physically active, and test their blood glucose. They may also need to take oral medication, and/or insulin to control blood glucose levels.
- As the risk of cardiovascular disease is much higher for a diabetic, it is crucial that blood pressure and cholesterol levels are monitored regularly.
- As smoking might have a serious effect on cardiovascular health, diabetics should stop smoking.
- Hypoglycemia – low blood glucose – can have a bad effect on the patient. Hyperglycemia – when blood glucose is too high – can also have a bad effect on the patient.
There are three types of diabetes:
1) Type 1 diabetes
The body does not produce insulin. Some people may refer to this type as insulin-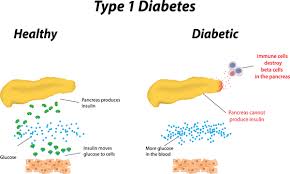 dependent diabetes, juvenile diabetes, orearly-onset diabetes. People usually develop type 1 diabetes before their 40th year, often in early adulthood or teenage years.
dependent diabetes, juvenile diabetes, orearly-onset diabetes. People usually develop type 1 diabetes before their 40th year, often in early adulthood or teenage years.
Type 1 diabetes is nowhere near as common as type 2 diabetes. Approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1.
Patients with type 1 diabetes will need to take insulin injections for the rest of their life. They must also ensure proper blood-glucose levels by carrying out regular blood tests and following a special diet.
2) Type 2 diabetes
The body does not produce enough insulin for proper function, or the cells in the body do not react to insulin (insulin resistance).
Approximately 90% of all cases of diabetes worldwide are type 2.

Some people may be able to control their type 2 diabetes symptoms by losing weight, following a healthy diet, doing plenty of exercise, and monitoring their blood glucose levels. However, type 2 diabetes is typically a progressive disease – it gradually gets worse – and the patient will probably end up have to take insulin, usually in tablet form.
Overweight and obese people have a much higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to those with a healthy body weight. People with a lot of visceral fat, also known as central obesity, belly fat, or abdominal obesity, are especially at risk. Being overweight/obese causes the body to release chemicals that can destabilize the body’s cardiovascular and metabolic systems.
Continue reading “Diabetes: This Ailment is dangerous to health”




 dia. He or she will probably take a sample from the cervix in women. Your doctor may also check for gonorrhea below, another STD. Some people with chlamydial also have gonorrhea.
dia. He or she will probably take a sample from the cervix in women. Your doctor may also check for gonorrhea below, another STD. Some people with chlamydial also have gonorrhea.

 the genital area are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and are known as genital, or venereal, warts.
the genital area are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and are known as genital, or venereal, warts. semen and vaginal fluids. Some people have no symptoms, which can delay diagnosis. Women suffer the most serious consequences of untreated disease – they can end up with pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility or a greater risk of ectopic pregnancy.
semen and vaginal fluids. Some people have no symptoms, which can delay diagnosis. Women suffer the most serious consequences of untreated disease – they can end up with pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility or a greater risk of ectopic pregnancy.
 available for the past 50 years. Syphilis has three distinct stages in an untreated person. During the first stage, a painless, open sore, called a chancre, appear on the genitals within a few weeks after infection. Usually just one shows up, although more are possible.
available for the past 50 years. Syphilis has three distinct stages in an untreated person. During the first stage, a painless, open sore, called a chancre, appear on the genitals within a few weeks after infection. Usually just one shows up, although more are possible.